Sony Unveils Energy Harvesting Chips. Sony Semiconductor Solutions (SSS) has introduced an innovative energy-harvesting module tailored for the Internet of Things (IoT), capable of capturing electromagnetic noise and converting it into usable power for sensors.
This groundbreaking module harnesses technology developed during SSS’s tuner development process, exhibiting remarkable efficiency in generating power from electromagnetic wave noise.
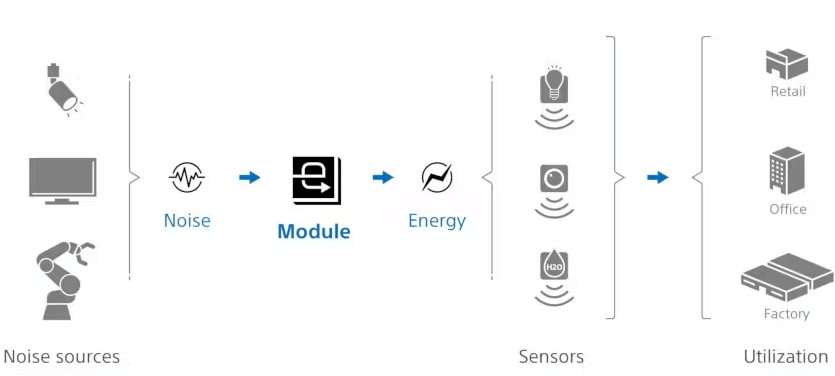
It leverages constant electromagnetic wave noise produced by various sources, such as factory robots, office equipment, monitors, lighting systems, and TVs, to deliver a reliable power supply for low-power IoT sensors and communication devices.
Sony Introduces Innovative Energy Harvester Utilizing Electromagnetic Wave Noise for IoT
Sony Unveils Energy Harvesting Chips. Energy harvesting has emerged as a pivotal solution to address the escalating demand for power among the multitude of small IoT nodes, each with modest power requirements.
While conventional energy harvesting methods tap into sources like solar energy and kinetic motion, Sony’s inventive approach centers on harnessing electromagnetic noise—unintentional emissions from devices like LED lighting, TV sets, and industrial robots.
Read More: National Incubation Center for Aerospace Technologies
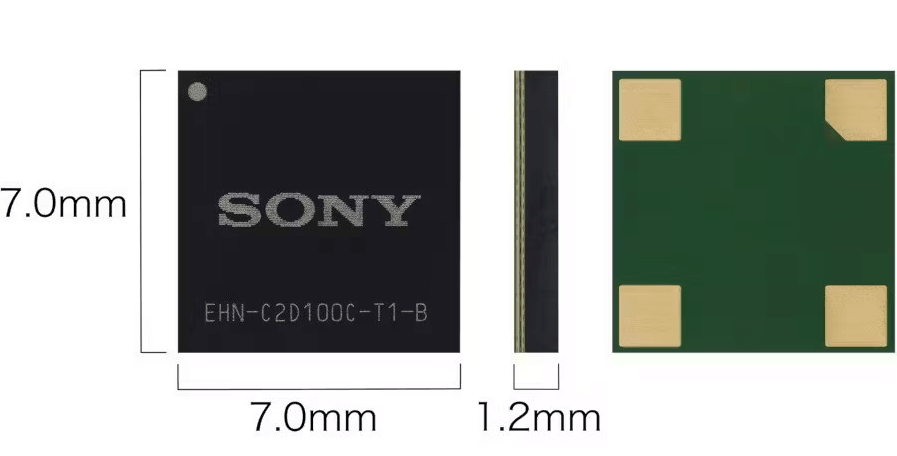
Sony’s compact energy-harvesting module, measuring 7×7mm (approximately 0.28×0.28″), ingeniously utilizes a device’s existing metal components as integral parts of a receiving antenna. Coupled with a high-efficiency rectifier circuit, this module can effectively capture electromagnetic noise spanning frequencies from “several Hz” to 100MHz.
This represents a pioneering achievement within the industry, marking the first energy-harvesting technology of its kind to attain such high efficiency. By efficiently utilizing previously overlooked electromagnetic wave noise as a novel power source, it facilitates a dependable power supply for various equipment.
Read More: Elon Musk`s Neural Link Valued at $5 Billion
Sony Unveils Energy Harvesting Chips: Future Prospects
While Sony has not yet disclosed detailed specifications, pricing, or availability for this module, the company affirms its capability to harvest power ranging from “several dozen μW to several dozen mW” from an array of common devices.
These devices include household appliances, computers, lighting systems, elevators, vehicles, and even vending machines, even when they are in standby mode but remain powered.
Notably, Sony envisions applications for this module as a remote sensor for predictive maintenance, capable of monitoring fluctuations in harvested energy levels to deduce the operational status of noise-generating devices.
Sony is enthusiastic about fostering collaborations with partners spanning diverse industries to develop innovative products based on this pioneering technology, offering tremendous potential across a broad spectrum of applications within the IoT landscape.
For more information, please visit Munafa Marketing.